首页 > Spring Cloud
阅读:213
Apollo服务端设计原理(源码解析)
本节主要对 Apollo 服务端设计原理进行解析。
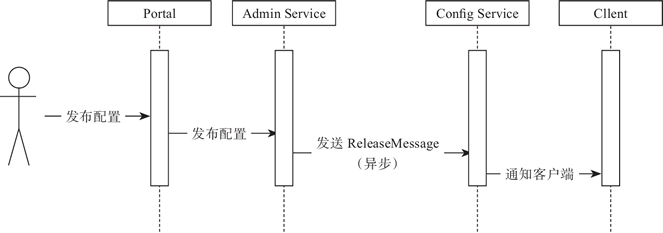
图 1 Apollo推送设计
图 1 简要描述了配置发布的大致过程。
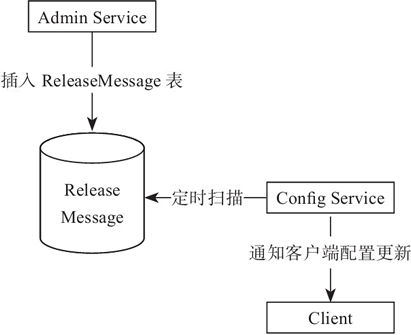
图 2 配置变化消息发送
图 2 简要描述了发送 ReleaseMessage 的大致过程:
当然,这些代码比较简单,很多细节就不做考虑了,只是为了能够让大家明白 Apollo 推送的核心原理。
发送 ReleaseMessage 的逻辑我们就写一个简单的接口,用队列存储,测试的时候就调用这个接口模拟配置有更新,发送 ReleaseMessage 消息。具体代码如下所示。
ReleaseMessage 就一个字段,模拟消息内容,具体代码如下所示。
NotificationControllerV2 实现了 ReleaseMessageListener 接口,ReleaseMessageListener 中定义了 handleMessage() 方法,具体代码如下所示。
如果 getApolloConfigNotifications() 方法没有返回配置修改的信息,则证明配置没有发生修改,那就将 DeferredResultWrapper 对象添加到 deferredResults 中,等待后续配置发生变化时消息监听器进行通知。
同时这个请求就会挂起,不会立即返回,挂起是通过 DeferredResultWrapper 中的下面这部分代码实现的,具体代码如下所示。
整个 Config Service 的流程就走完了,接下来我们来看一下客户端是怎么实现的,我们简单地写一个测试类模拟客户端注册,具体代码如下所示。
每次收到结果后,无论是有修改还是无修改,都必须重新进行注册,通过这样的方式就可以达到配置实时推送的效果。
我们可以调用之前写的 /addMsg 接口来模拟配置发生变化,调用之后客户端就能马上得到返回结果。
1. 配置发布后的实时推送设计
配置中心最重要的一个特性就是实时推送,正因为有这个特性,我们才可以依赖配置中心做很多事情。如图 1 所示。
图 1 Apollo推送设计
图 1 简要描述了配置发布的大致过程。
- 用户在 Portal 中进行配置的编辑和发布。
- Portal 会调用 Admin Service 提供的接口进行发布操作。
- Admin Service 收到请求后,发送 ReleaseMessage 给各个 Config Service,通知 Config Service 配置发生变化。
- Config Service 收到 ReleaseMessage 后,通知对应的客户端,基于 Http 长连接实现。
2. 发送 ReleaseMessage 的实现方式
ReleaseMessage 消息是通过 Mysql 实现了一个简单的消息队列。之所以没有采用消息中间件,是为了让 Apollo 在部署的时候尽量简单,尽可能减少外部依赖,如图 2 所示。
图 2 配置变化消息发送
图 2 简要描述了发送 ReleaseMessage 的大致过程:
- Admin Service 在配置发布后会往 ReleaseMessage 表插入一条消息记录。
- Config Service 会启动一个线程定时扫描 ReleaseMessage 表,来查看是否有新的消息记录。
- Config Service 发现有新的消息记录,就会通知到所有的消息监听器。
- 消息监听器得到配置发布的信息后,就会通知对应的客户端。
3. Config Service 通知客户端的实现方式
通知采用基于 Http 长连接实现,主要分为下面几个步骤:- 客户端会发起一个 Http 请求到 Config Service 的 notifications/v2 接口。
- notifications/v2 接口通过 Spring DeferredResult 把请求挂起,不会立即返回。
- 如果在 60s 内没有该客户端关心的配置发布,那么会返回 Http 状态码 304 给客户端。
- 如果发现配置有修改,则会调用 DeferredResult 的 setResult 方法,传入有配置变化的 namespace 信息,同时该请求会立即返回。
- 客户端从返回的结果中获取到配置变化的 namespace 后,会立即请求 Config Service 获取该 namespace 的最新配置。
4. 源码解析实时推送设计
Apollo 推送涉及的代码比较多,本教程就不做详细分析了,笔者把推送这里的代码稍微简化了下,给大家进行讲解,这样理解起来会更容易。当然,这些代码比较简单,很多细节就不做考虑了,只是为了能够让大家明白 Apollo 推送的核心原理。
发送 ReleaseMessage 的逻辑我们就写一个简单的接口,用队列存储,测试的时候就调用这个接口模拟配置有更新,发送 ReleaseMessage 消息。具体代码如下所示。
@RestController
public class NotificationControllerV2 implements ReleaseMessageListener {
// 模拟配置更新, 向其中插入数据表示有更新
public static Queue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>();
@GetMapping("/addMsg")
public String addMsg() {
queue.add("xxx");
return "success";
}
}
消息发送之后,根据前面讲过的 Config Service 会启动一个线程定时扫描 ReleaseMessage 表,查看是否有新的消息记录,然后取通知客户端,在这里我们也会启动一个线程去扫描,具体代码如下所示。
@Component
public class ReleaseMessageScanner implements InitializingBean {
@Autowired
private NotificationControllerV2 configController;
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
// 定时任务从数据库扫描有没有新的配置发布
new Thread(() -> {
for (;;) {
String result = NotificationControllerV2.queue.poll();
if (result != null) {
ReleaseMessage message = new ReleaseMessage();
message.setMessage(result);
configController.handleMessage(message);
}
}
}).start();
;
}
}
循环读取 NotificationControllerV2 中的队列,如果有消息的话就构造一个 Release-Message 的对象,然后调用 NotificationControllerV2 中的 handleMessage() 方法进行消息的处理。ReleaseMessage 就一个字段,模拟消息内容,具体代码如下所示。
public class ReleaseMessage {
private String message;
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}
接下来,我们来看 handleMessage 做了哪些工作。NotificationControllerV2 实现了 ReleaseMessageListener 接口,ReleaseMessageListener 中定义了 handleMessage() 方法,具体代码如下所示。
public interface ReleaseMessageListener {
void handleMessage(ReleaseMessage message);
}
@RestController
public class NotificationControllerV2 implements ReleaseMessageListener {
private final Multimap<String, DeferredResultWrapper> deferredResults = Multimaps
.synchronizedSetMultimap(HashMultimap.create());
@Override
public void handleMessage(ReleaseMessage message) {
System.err.println("handleMessage:" + message);
List<DeferredResultWrapper> results = Lists.newArrayList(deferredResults.get("xxxx"));
for (DeferredResultWrapper deferredResultWrapper : results) {
List<ApolloConfigNotification> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new ApolloConfigNotification("application", 1));
deferredResultWrapper.setResult(list);
}
}
}
Apollo 的实时推送是基于 Spring DeferredResult 实现的,在 handleMessage() 方法中可以看到是通过 deferredResults 获取 DeferredResult,deferredResults 就是第一行的 Multimap,Key 其实就是消息内容,Value 就是 DeferredResult 的业务包装类 DeferredResultWrapper,我们来看下 DeferredResultWrapper 的代码,代码如下所示。
public class DeferredResultWrapper {
private static final long TIMEOUT = 60 * 1000;// 60 seconds
private static final ResponseEntity<List<ApolloConfigNotification>> NOT_MODIFIED_RESPONSE_LIST = new ResponseEntity<>(
HttpStatus.NOT_MODIFIED);
private DeferredResult<ResponseEntity<List<ApolloConfigNotification>>> result;
public DeferredResultWrapper() {
result = new DeferredResult<>(TIMEOUT, NOT_MODIFIED_RESPONSE_LIST);
}
public void onTimeout(Runnable timeoutCallback) {
result.onTimeout(timeoutCallback);
}
public void onCompletion(Runnable completionCallback) {
result.onCompletion(completionCallback);
}
public void setResult(ApolloConfigNotification notification) {
setResult(Lists.newArrayList(notification));
}
public void setResult(List<ApolloConfigNotification> notifications) {
result.setResult(new ResponseEntity<>(notifications, HttpStatus.OK));
}
public DeferredResult<ResponseEntity<List<ApolloConfigNotification>>> getResult() {
return result;
}
}
通过 setResult() 方法设置返回结果给客户端,以上就是当配置发生变化,然后通过消息监听器通知客户端的原理,那么客户端是在什么时候接入的呢?具体代码如下。
@RestController
public class NotificationControllerV2 implements ReleaseMessageListener {
// 模拟配置更新, 向其中插入数据表示有更新
public static Queue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>();
private final Multimap<String, DeferredResultWrapper> deferredResults = Multimaps
.synchronizedSetMultimap(HashMultimap.create());
@GetMapping("/getConfig")
public DeferredResult<ResponseEntity<List<ApolloConfigNotification>>> getConfig() {
DeferredResultWrapper deferredResultWrapper = new DeferredResultWrapper();
List<ApolloConfigNotification> newNotifications = getApolloConfigNotifications();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(newNotifications)) {
deferredResultWrapper.setResult(newNotifications);
} else {
deferredResultWrapper.onTimeout(() -> {
System.err.println("onTimeout");
});
deferredResultWrapper.onCompletion(() -> {
System.err.println("onCompletion");
});
deferredResults.put("xxxx", deferredResultWrapper);
}
return deferredResultWrapper.getResult();
}
private List<ApolloConfigNotification> getApolloConfigNotifications() {
List<ApolloConfigNotification> list = new ArrayList<>();
String result = queue.poll();
if (result != null) {
list.add(new ApolloConfigNotification("application", 1));
}
return list;
}
}
NotificationControllerV2 中提供了一个 /getConfig 的接口,客户端在启动的时候会调用这个接口,这个时候会执行 getApolloConfigNotifications() 方法去获取有没有配置的变更信息,如果有的话证明配置修改过,直接就通过 deferredResultWrapper.setResult(newNotifications) 返回结果给客户端,客户端收到结果后重新拉取配置的信息覆盖本地的配置。如果 getApolloConfigNotifications() 方法没有返回配置修改的信息,则证明配置没有发生修改,那就将 DeferredResultWrapper 对象添加到 deferredResults 中,等待后续配置发生变化时消息监听器进行通知。
同时这个请求就会挂起,不会立即返回,挂起是通过 DeferredResultWrapper 中的下面这部分代码实现的,具体代码如下所示。
private static final long TIMEOUT = 60 * 1000; // 60 seconds
private static final ResponseEntity<List<ApolloConfigNotification>> NOT_MODIFIED_RESPONSE_LIST = new ResponseEntity<>(
HttpStatus.NOT_MODIFIED);
private DeferredResult<ResponseEntity<List<ApolloConfigNotification>>> result;
public DeferredResultWrapper() {
result = new DeferredResult<>(TIMEOUT, NOT_MODIFIED_RESPONSE_LIST);
}
在创建 DeferredResult 对象的时候指定了超时的时间和超时后返回的响应码,如果 60s 内没有消息监听器进行通知,那么这个请求就会超时,超时后客户端收到的响应码就是 304。整个 Config Service 的流程就走完了,接下来我们来看一下客户端是怎么实现的,我们简单地写一个测试类模拟客户端注册,具体代码如下所示。
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
reg();
}
private static void reg() {
System.err.println("注册");
String result = request("http://localhost:8081/getConfig");
if (result != null) {
// 配置有更新, 重新拉取配置
// ......
}
// 重新注册
reg();
}
private static String request(String url) {
HttpURLConnection connection = null;
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
URL getUrl = new URL(url);
connection = (HttpURLConnection) getUrl.openConnection();
connection.setReadTimeout(90000);
connection.setConnectTimeout(3000);
connection.setRequestMethod("GET");
connection.setRequestProperty("Accept-Charset", "utf-8");
connection.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/json");
connection.setRequestProperty("Charset", "UTF-8");
System.out.println(connection.getResponseCode());
if (200 == connection.getResponseCode()) {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(connection.getInputStream(), "UTF-8"));
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
result.append(line);
}
System.out.println("结果 " + result);
return result.toString();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (connection != null) {
connection.disconnect();
}
}
return null;
}
}
首先启动 /getConfig 接口所在的服务,然后启动客户端,然后客户端就会发起注册请求,如果有修改直接获取到结果,则进行配置的更新操作。如果无修改,请求会挂起,这里客户端设置的读取超时时间是 90s,大于服务端的 60s 超时时间。每次收到结果后,无论是有修改还是无修改,都必须重新进行注册,通过这样的方式就可以达到配置实时推送的效果。
我们可以调用之前写的 /addMsg 接口来模拟配置发生变化,调用之后客户端就能马上得到返回结果。
所有教程
- socket
- Python基础教程
- C#教程
- MySQL函数
- MySQL
- C语言入门
- C语言专题
- C语言编译器
- C语言编程实例
- GCC编译器
- 数据结构
- C语言项目案例
- C++教程
- OpenCV
- Qt教程
- Unity 3D教程
- UE4
- STL
- Redis
- Android教程
- JavaScript
- PHP
- Mybatis
- Spring Cloud
- Maven
- vi命令
- Spring Boot
- Spring MVC
- Hibernate
- Linux
- Linux命令
- Shell脚本
- Java教程
- 设计模式
- Spring
- Servlet
- Struts2
- Java Swing
- JSP教程
- CSS教程
- TensorFlow
- 区块链
- Go语言教程
- Docker
- 编程笔记
- 资源下载
- 关于我们
- 汇编语言
- 大数据
- 云计算
- VIP视频
