Scale your cluster
Estimated reading time: 5 minutesThese are the docs for UCP version 2.2.4
To select a different version, use the selector below.
Docker UCP is designed for scaling horizontally as your applications grow in size and usage. You can add or remove nodes from the UCP cluster to make it scale to your needs.
Since UCP leverages the clustering functionality provided by Docker Engine, you use the docker swarm join command to add more nodes to your cluster. When joining new nodes, the UCP services automatically start running in that node.
When joining a node to a cluster you can specify its role: manager or worker.
-
Manager nodes
Manager nodes are responsible for swarm management functionality and dispatching tasks to worker nodes. Having multiple manager nodes allows your swarm to be highly-available and tolerate node failures.
Manager nodes also run all UCP components in a replicated way, so by adding additional manager nodes, you’re also making UCP highly available. Learn more about the UCP architecture.
-
Worker nodes
Worker nodes receive and execute your services and applications. Having multiple worker nodes allows you to scale the computing capacity of your cluster.
When deploying Docker Trusted Registry in your cluster, you deploy it to a worker node.
Join nodes to the cluster
To join nodes to the swarm, go to the UCP web UI and navigate to the Nodes page.
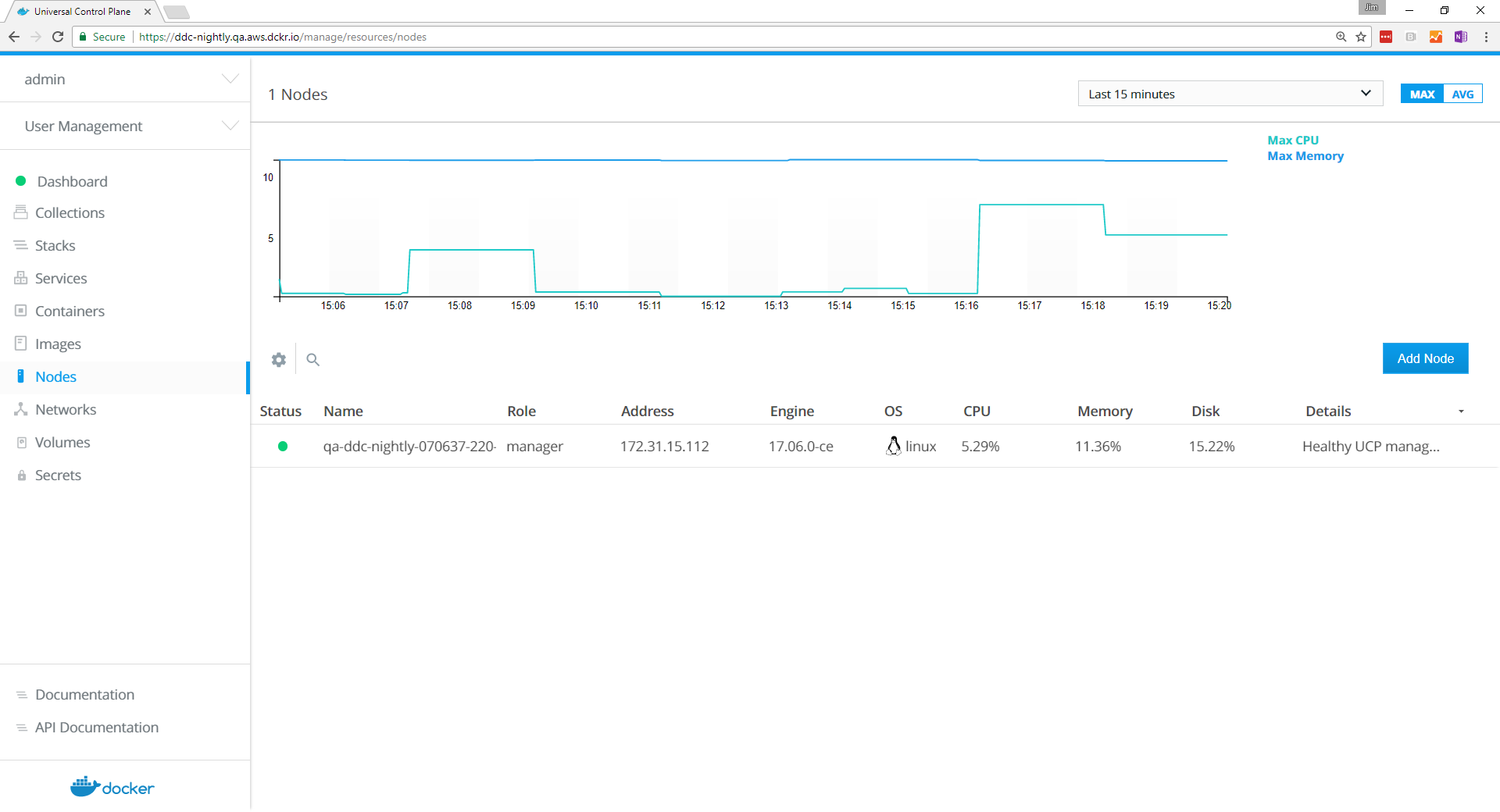
Click Add Node to add a new node.
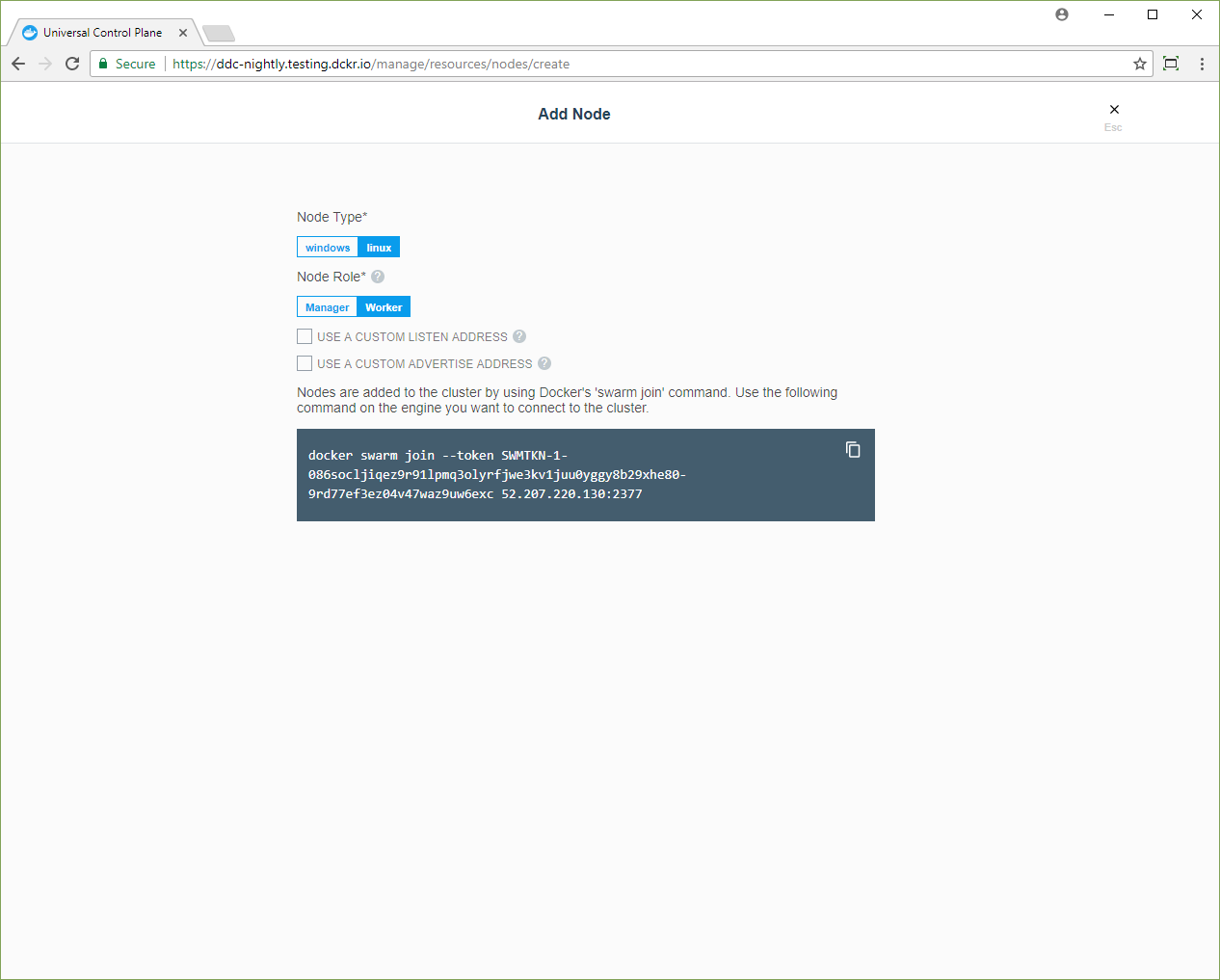
- Click Manager if you want to add the node as a manager.
- Check the Use a custom listen address option to specify the IP address of the host that you’ll be joining to the cluster.
- Check the Use a custom listen address option to specify the IP address that’s advertised to all members of the swarm for API access.
Copy the displayed command, use ssh to log into the host that you want to
join to the cluster, and run the docker swarm join command on the host.
To add a Windows node, click Windows and follow the instructions in Join Windows worker nodes to a swarm.
After you run the join command in the node, the node is displayed in the UCP web UI.
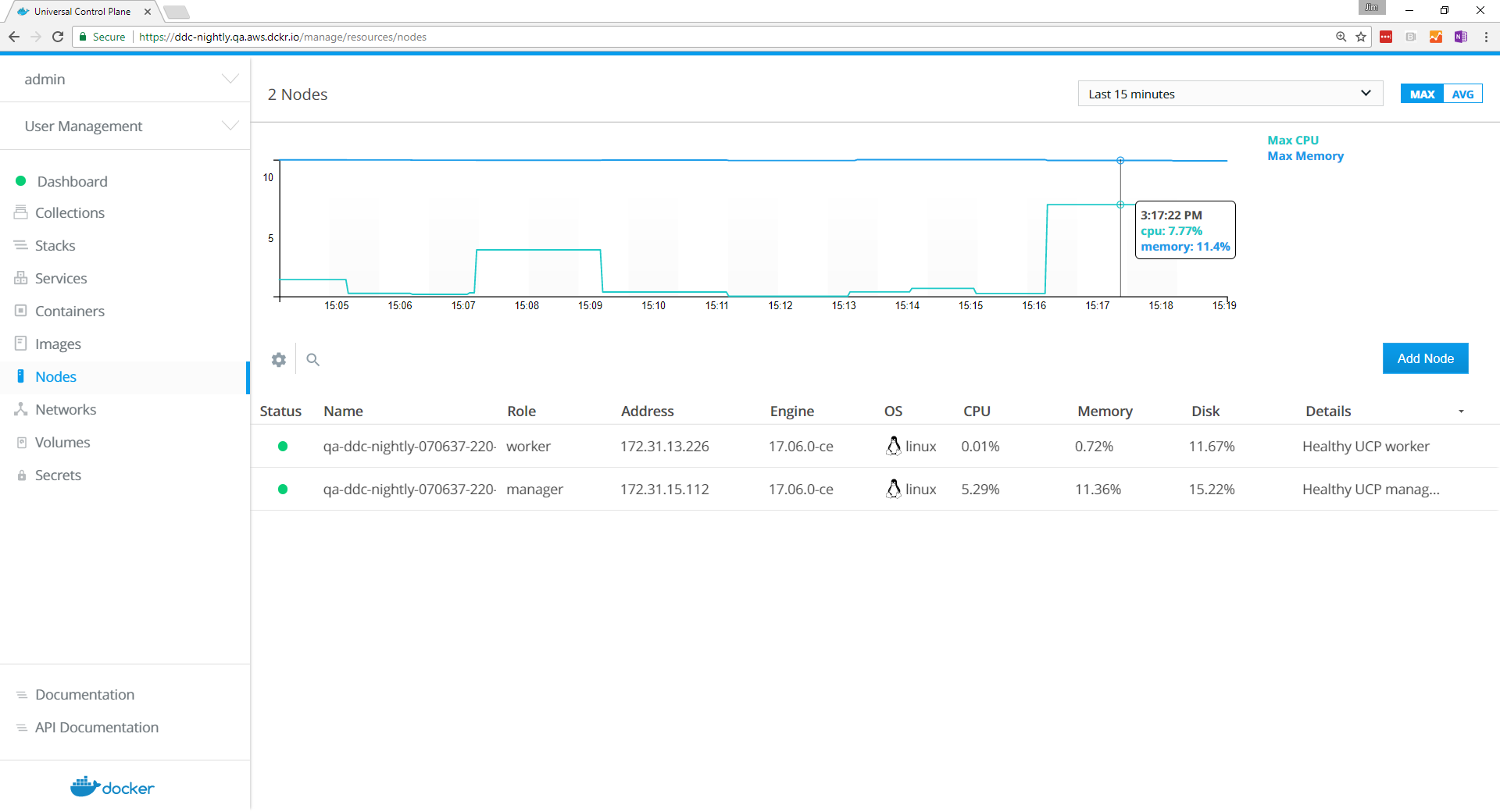
Remove nodes from the cluster
- If the target node is a manager, you will need to first demote the node into
a worker before proceeding with the removal:
- From the UCP web UI, navigate to the Nodes page. Select the node you wish to remove and switch its role to Worker, wait until the operation completes, and confirm that the node is no longer a manager.
- From the CLI, perform
docker node lsand identify the nodeID or hostname of the target node. Then, rundocker node demote <nodeID or hostname>.
-
If the status of the worker node is
Ready, you’ll need to manually force the node to leave the swarm. To do this, connect to the target node through SSH and rundocker swarm leave --forcedirectly against the local docker engine.Loss of quorum
Do not perform this step if the node is still a manager, as this may cause loss of quorum.
- Now that the status of the node is reported as
Down, you may remove the node:- From the UCP web UI, browse to the Nodes page and select the node. In the details pane, click Actions and select Remove. Click Confirm when you’re prompted.
- From the CLI, perform
docker node rm <nodeID or hostname>.
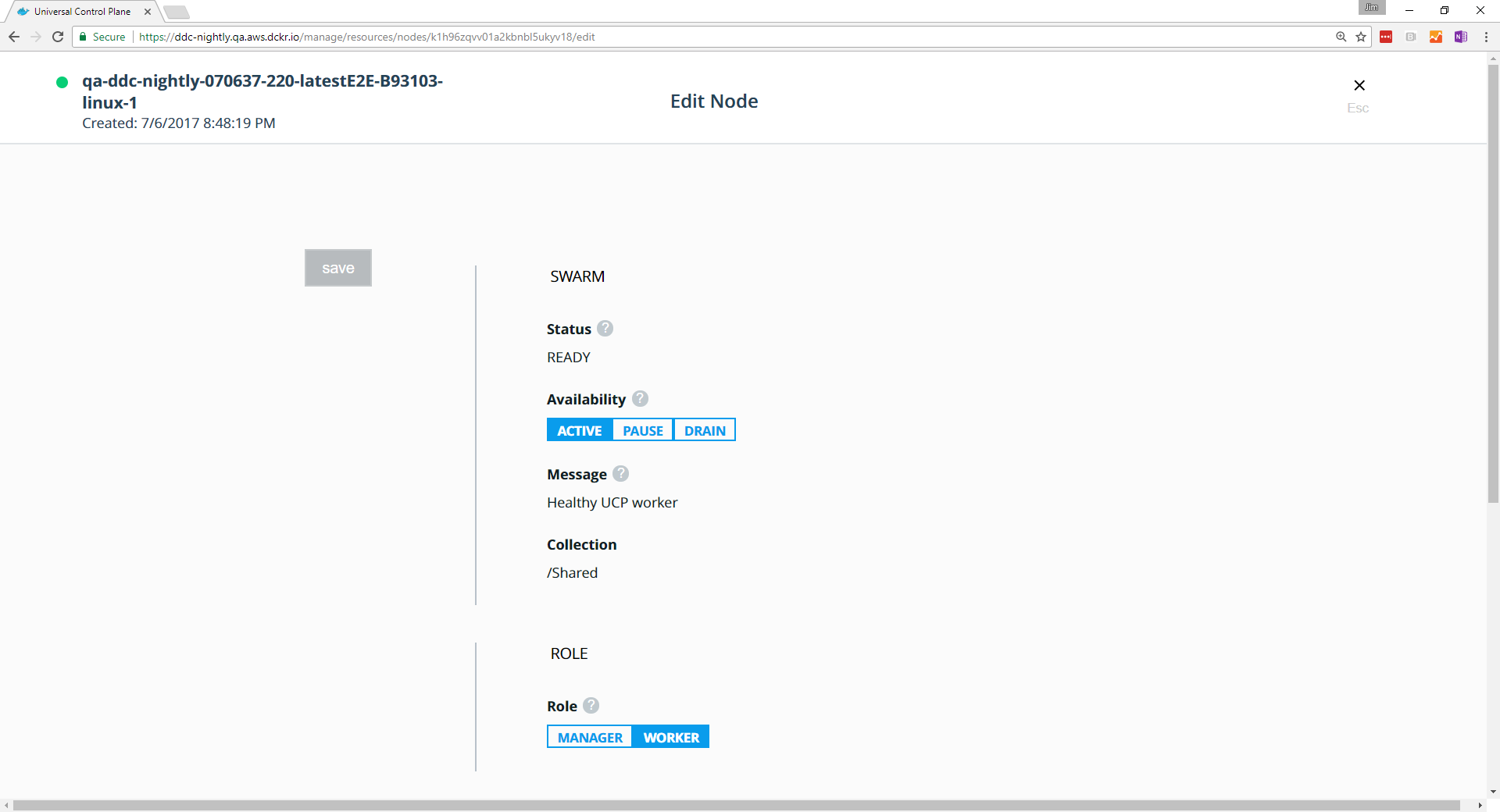
Pause and drain nodes
Once a node is part of the cluster you can change its role making a manager node into a worker and vice versa. You can also configure the node availability so that it is:
- Active: the node can receive and execute tasks.
- Paused: the node continues running existing tasks, but doesn’t receive new ones.
- Drained: the node won’t receive new tasks. Existing tasks are stopped and replica tasks are launched in active nodes.
In the UCP web UI, browse to the Nodes page and select the node. In the details pane, click the Configure to open the Edit Node page.
If you’re load-balancing user requests to UCP across multiple manager nodes, when demoting those nodes into workers, don’t forget to remove them from your load-balancing pool.
Scale your cluster from the CLI
You can also use the command line to do all of the above operations. To get the join token, run the following command on a manager node:
$ docker swarm join-token worker
If you want to add a new manager node instead of a worker node, use
docker swarm join-token manager instead. If you want to use a custom listen
address, add the --listen-addr arg:
$ docker swarm join \
--token SWMTKN-1-2o5ra9t7022neymg4u15f3jjfh0qh3yof817nunoioxa9i7lsp-dkmt01ebwp2m0wce1u31h6lmj \
--listen-addr 234.234.234.234 \
192.168.99.100:2377
Once your node is added, you can see it by running docker node ls on a manager:
$ docker node ls
To change the node’s availability, use:
$ docker node update --availability drain node2
You can set the availability to active, pause, or drain.
To remove the node, use:
$ docker node rm <node-hostname>
