Docker Store trust chain
Estimated reading time: 2 minutesFor consumers
Docker ensures that all content is securely received and verified from original producers, and additionally audits images before adding them to the Docker Store. Docker cryptographically signs the images upon completion of a satisfactory image check, so that you can verify and trust certified content from the Docker Store.
Here’s the full trust chain in detail, with details on how to cryptographically verify completion of the process when pulling an image from Docker Store:
-
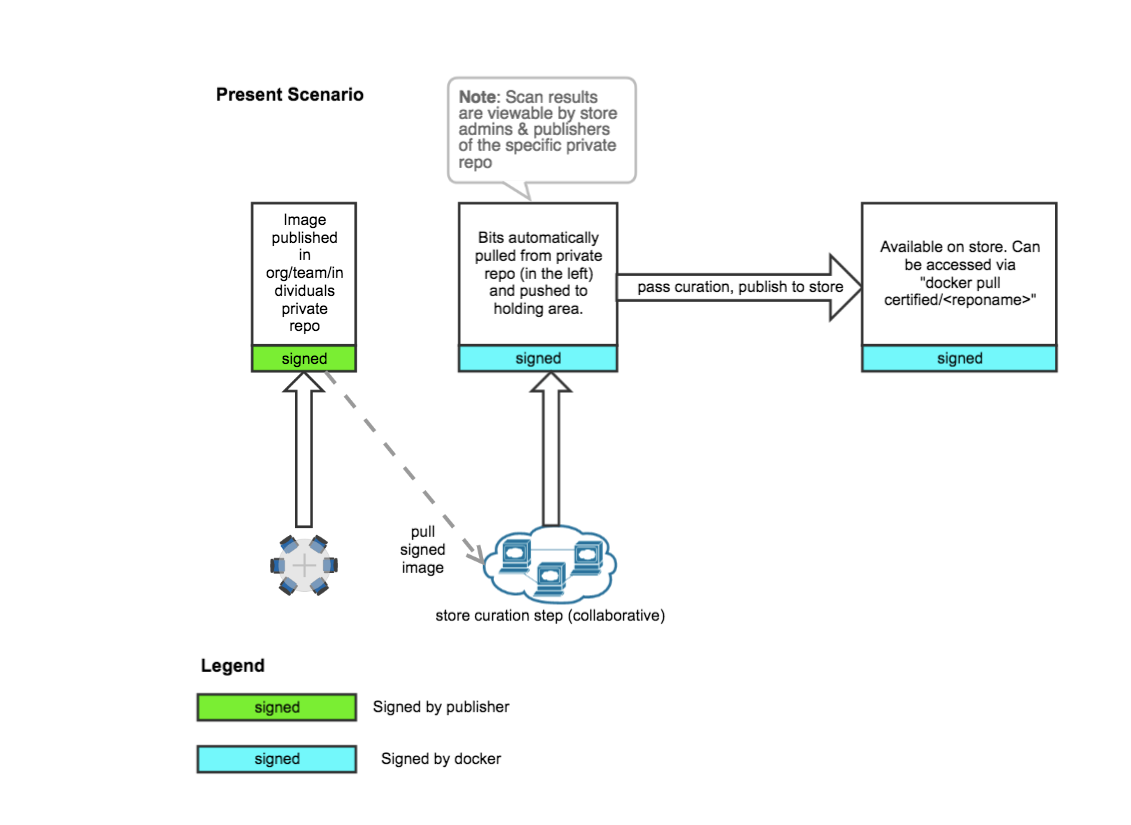
Producers sign and push their images using Docker Content Trust to a private staging area.
-
Docker pulls the image, verifies the signatures to guarantee authenticity, integrity, and freshness of the image.
-
The Docker Store certification team performs a thorough review of the image, looking for vulnerabilities and verifying best practices for image hygiene, such as ensuring minimal image sizes and working health-checks.
-
Upon a successful review, Docker signs the image and makes it officially available on Docker Store. As a consumer, you can confirm that Docker signed the image by pulling and running with Docker Content Trust:
DOCKER_CONTENT_TRUST=1 docker pull <image> DOCKER_CONTENT_TRUST=1 docker run <image>
For producers
The Docker Store has a thorough and well-defined certification process to ensure top-quality content from producers is delivered to consumers in a trusted manner. As a producer of content, you will be required to sign your images so that Docker can verify that your content is not tampered with upon starting the image certification and publishing process as outlined below:
-
Producers sign and push their images using Docker Content Trust to a private staging area. To do this, run a
docker pushcommand with Content Trust enabled:DOCKER_CONTENT_TRUST=1 docker pull <image> -
Docker verifies the signatures to guarantee authenticity, integrity, and freshness of the image. All of the individual layers of your image, and the combination thereof, are encompassed as part of this verification check. Read more detail about Content Trust in Docker’s documentation.
-
Upon a successful signature verification, Docker pulls the original image to a private, internal staging area only accessible to the Docker Store certification team.
-
The Docker Store certification team performs a thorough review of the image, looking for vulnerabilities and verifying best practices for image hygiene, such as ensuring minimal image sizes and working health-checks.
-
Upon a successful review, Docker signs the image and makes it officially available on Docker Store. Similar to artifacts on the Apple Store, this is the final and only signature on the image. Your consumers confirm that the full certification process was completed by checking Docker’s signature by pulling and running with Docker Content Trust:
DOCKER_CONTENT_TRUST=1 docker pull <image> DOCKER_CONTENT_TRUST=1 docker run <image>
To learn more the trust chain and certification for publishing content, see Security and Audit Policies in the publishers guide.
trust, chain, store