Manage service stacks
Estimated reading time: 4 minutesA stack is a collection of services that make up an application in a specific environment. A stack file is a file in YAML format, similar to a docker-compose.yml file, that defines one or more services. The YAML reference is documented here.
Stacks are a convenient way to automatically deploy multiple services that are linked to each other, without needing to define each one separately.
Stack files define environment variables, deployment tags, the number of containers, and related environment-specific configuration. Because of this, you should use a separate stack file for development, staging, production, and other environments.
Stack file example
Below is an example docker-cloud.yml:
lb:
image: dockercloud/haproxy
links:
- web
ports:
- "80:80"
roles:
- global
web:
image: dockercloud/quickstart-python
links:
- redis
target_num_containers: 4
redis:
image: redis
Each key defined in docker-cloud.yml creates a service with that name in Docker Cloud. In the example above, three services are created: lb, web and redis. Each service is a dictionary and its keys are specified below.
Only the image key is mandatory. Other keys are optional and are analogous to their Docker Cloud Service API counterparts.
Create a stack
Docker Cloud allows you to create stacks from the web interface, as well as via the Docker Cloud API and the docker-cloud command line.
To create a stack from the Docker Cloud web interface:
- Log in to Docker Cloud.
- Click Stacks.
- Click Create.
- Enter a name for the stackfile.
-
Enter or paste the stack file in the Stackfile field, or drag a file to the field to upload it. (You can also click in the field to browse for and upload a file on your computer.)
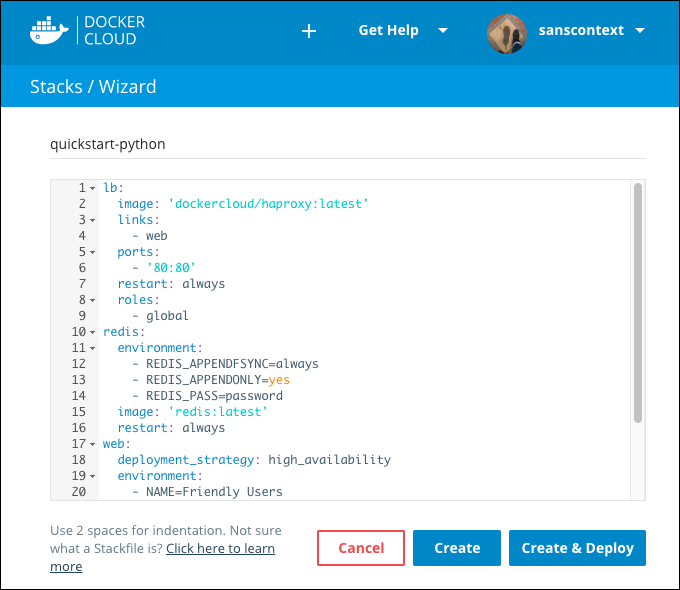
- Click Create or Create and deploy.
Create a stack using the API
You can also create a new stack by uploading a stack file directly using the Docker Cloud API. When you use the API, the stack file has to be in JSON format, like the following example:
POST /api/v1/stack/ HTTP/1.1
{
"name": "my-new-stack",
"services": [
{
"name": "hello-word",
"image": "dockercloud/hello-world",
"target_num_containers": 2
}
]
}
Check our API documentation for more information.
Create a stack using the CLI
You can create a stack from a YAML file by executing:
$ docker-cloud stack create -f docker-cloud.yml
Check our CLI documentation for more information.
Update an existing stack
You can specify an existing stack when you create a service, however you might not always have the stack definition ready at that time, or you might later want to add a service to an existing stack.
To update a stack from the Docker Cloud web interface:
- Navigate to the stack you want to update.
-
Click Edit.
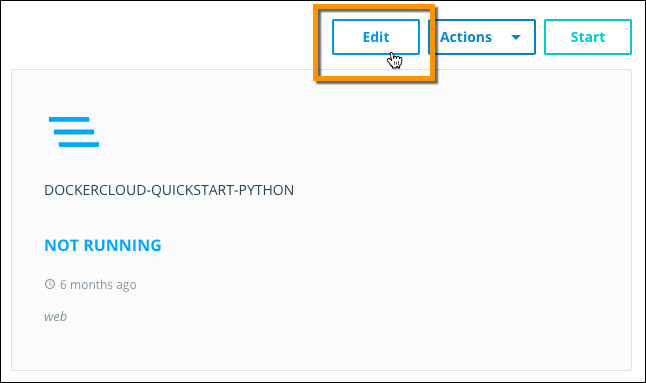
- Edit the stack file, or upload a new one from your computer.
- Click Save.
Update an existing stack using the API
You can also update a stack by uploading the new stack file directly using the Docker Cloud API. When you use the API, the stack file has to be in JSON format, like the following example:
PATCH /api/app/v1/stack/(uuid)/ HTTP/1.1
{
"services": [
{
"name": "hello-word",
"image": "dockercloud/hello-world",
"target_num_containers": 2
}
]
}
Check our API documentation for more information.
Update an existing stack using the CLI
You can update a stack from a YAML file by executing:
docker-cloud stack update -f docker-cloud.yml (uuid or name)
Check our CLI documentation for more information.
service, stack, yaml